|
Para la versión en español, haga clic aquí
Our fans in South America frequently send us messages requesting we don't neglect the airports on their beautiful and amazing continent. They are right of course, and today we will start correcting the record!
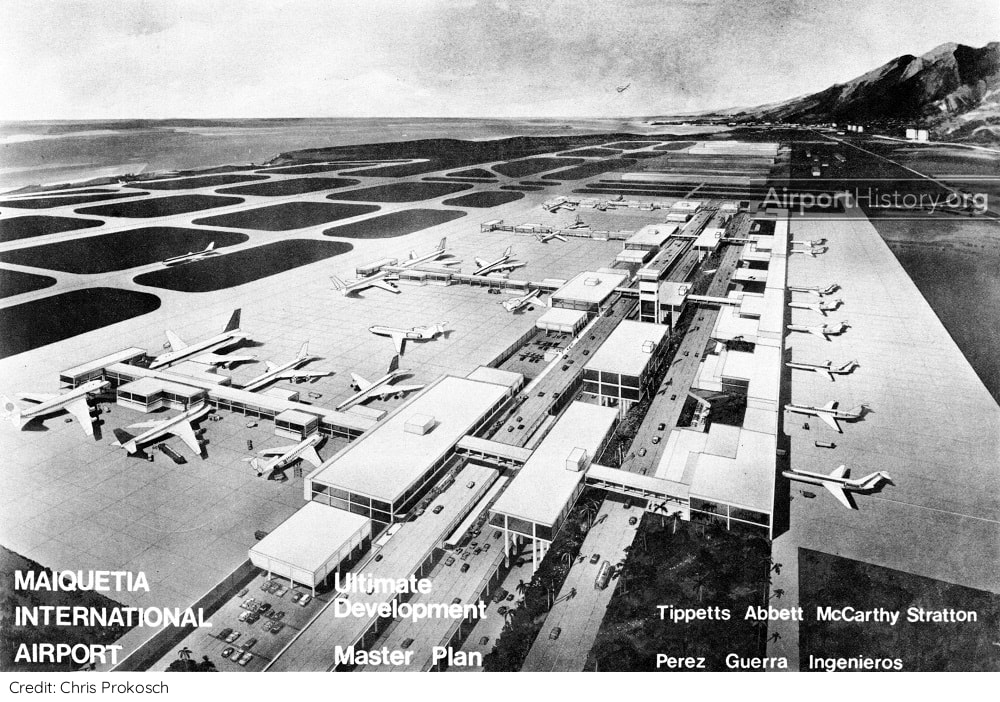
Deep in the AirportHistory.org vault, we recently found the 1969 Master Plan for Maiquetía "Simón Bolívar" International Airport, the main international gateway for Venezuela. In the mid-20th century, Venezuela was a booming oil country. With air travel rapidly growing and money being plentiful, the government planned for a huge expansion project, which was only partially implemented. Curious about what the planners originally had in mind for the future of Maiquetía? Without further ado, let's take a look!
A SHORT HISTORY
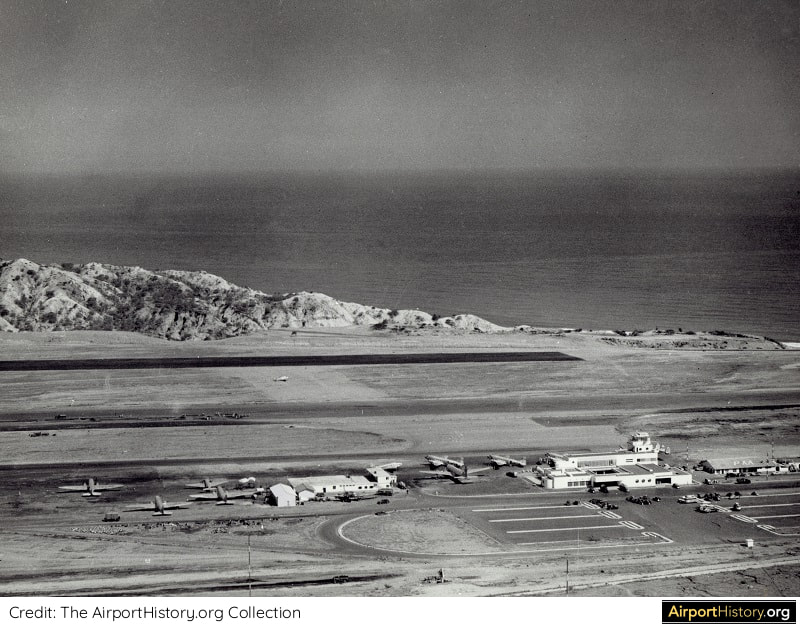
Known originally as La Guaira Airport, the airport was constructed in 1930 by Pan American Airways. By 1949, it had a 5,000-foot (1,524-meter) runway, which was later extended to 9,842 feet (3,000 meters). The original terminal building, toward the eastern end of the airport, was opened in 1948.
MASTER PLAN
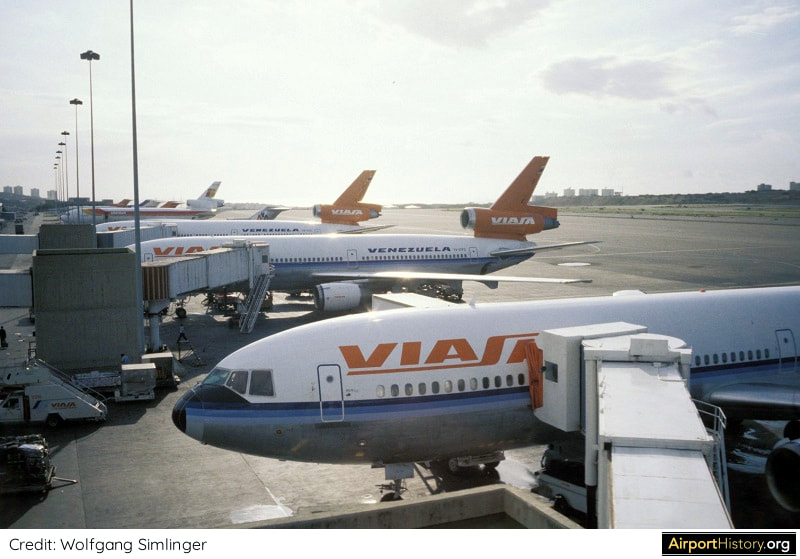
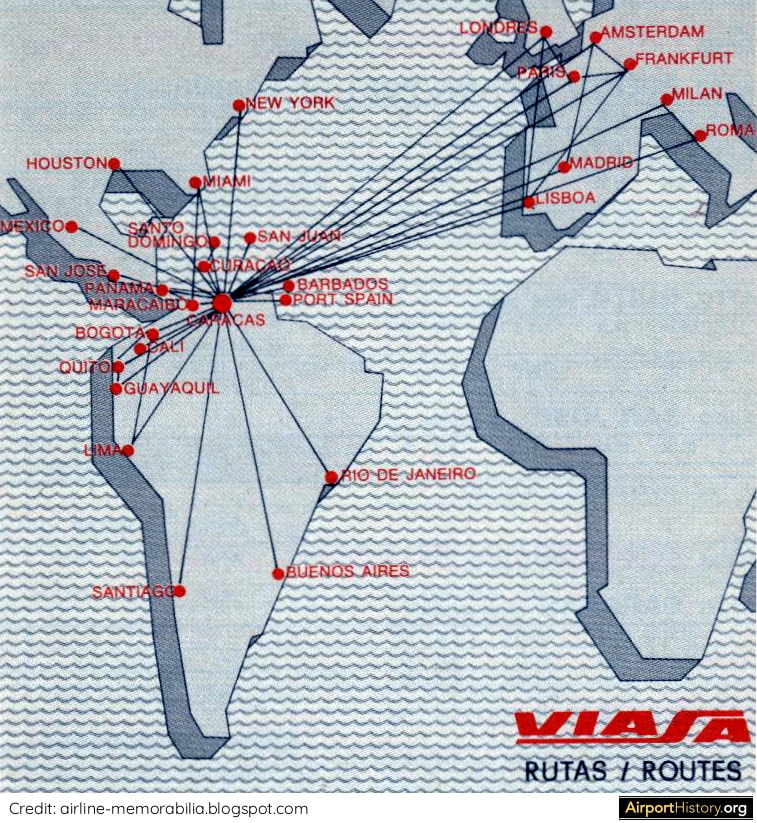
By 1970, Maiquetía was handling 1.47 million passengers, making it the third busiest airport in South America, after Bogota El Dorado and São Paulo Congonas airports. Since its founding in 1960, VIASA, Venezuela's national airline, had quickly developed into of South America's premier airlines, connecting cities in South America, North America, and Europe. The airline needed a home airport that could accomodate its growth ambitions. In 1968, the government engaged the services of the renowned firm Tibbetts, Abbott, McCarthy, and Stratton (TAMS) to prepare plans for Maiquetía's future development.
Did you know?
One of the experts in charge of the Maiquetía Master Plan Project was Walther Prokosch, the architect who led the design of the legendary Pan Am terminal at JFK Airport and the Master Plan for DFW Airport.
NEW RUNWAYS
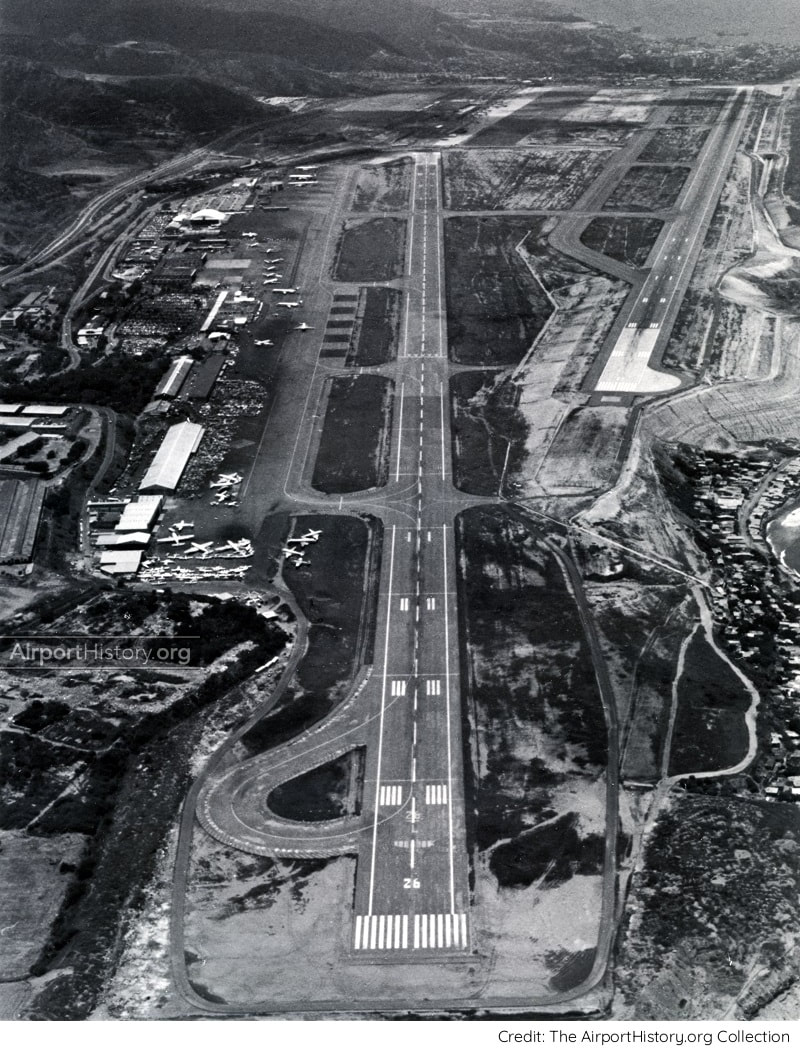
Traffic studies projected that Maiquetía would handle 30 million passengers by the year 2000, 20 times more than in 1970, thus requiring a radical expansion of the airport. Planners envisaged a large-scale expansion of the airport to the west with two new runways and a new passenger terminal complex. First, a new 11,483-foot (3,500-meter) runway 09/27 would be built between the original runway 08/26 and the sea. Its consctruction would involve moving 650 million cubic feet of earth. The runway was commissioned in 1975. Later on, a second runway would be built 705 feet (215 meters) to the north and west of runway 09/27. It would have a full length taxiway and its construction would involve the removal of a series of hills beside the shore. The runway was to be completed in the early 1980s, after which the original runway 08/26 would likely be closed.
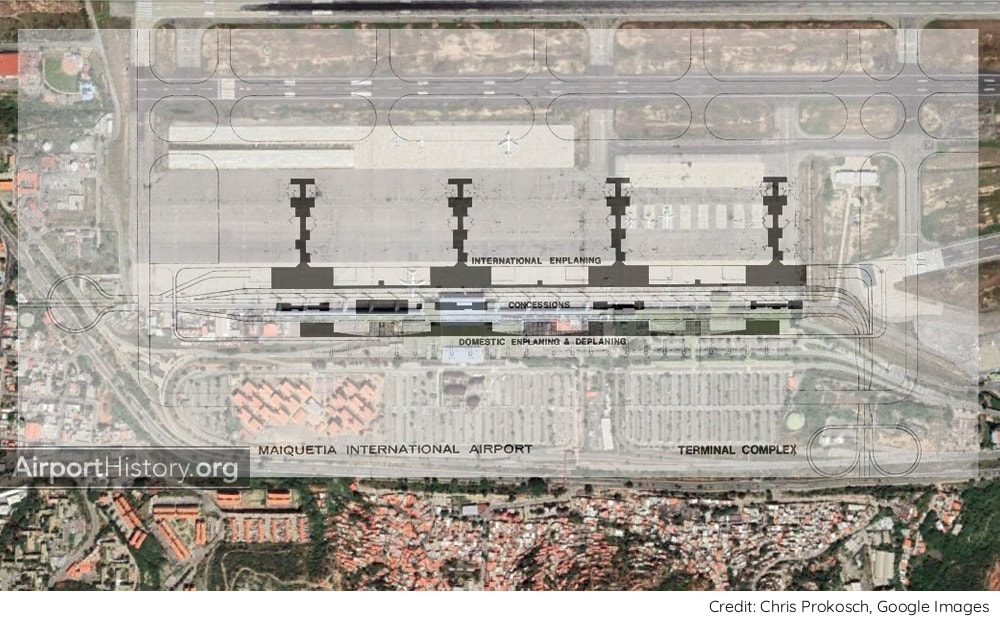
TERMINALS
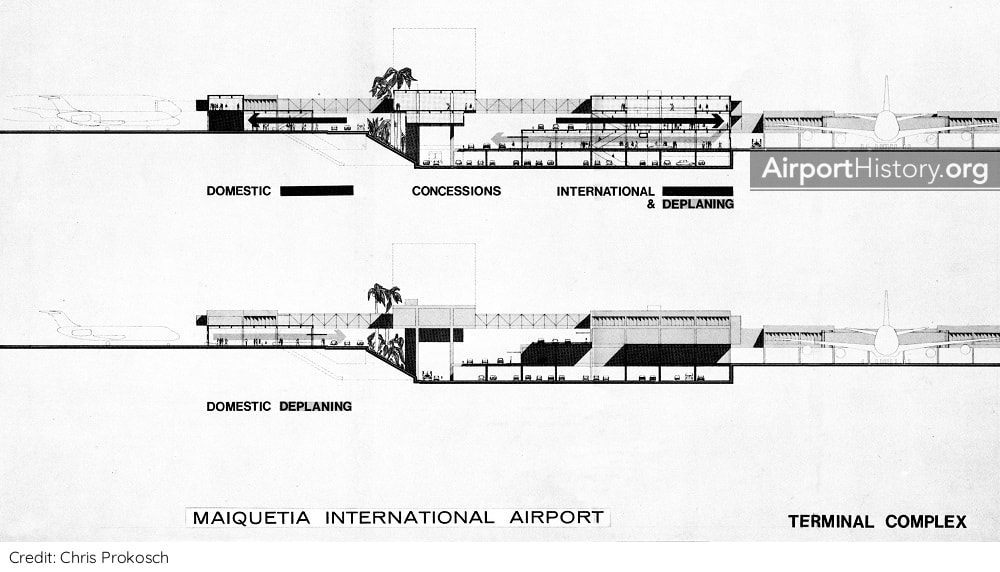
In the ultimate layout, planners envisaged a series of passenger terminal buildings built along a spine road. To the north would be four terminal modules handling international flights. On the south side--the mountain side--would be an elongated terminal building handling domestic flights. A total of 48 gates served by passenger boarding bridges would be provided: 24 international gates and 24 domestic gates. The international and domestic sides would be connected by buildings in the median of the spine road, which contained concessions. There would be parking space for 2,800 cars. The complex was too small to justify an automated people mover shuttle but space was left in the design to construct one eventually if needed.
Want more stunning airport photos & stories?
Sign up to our newsletter below to know when new content goes online.
PHASED DEVELOPMENT
Initially, all development would take place on the north side with separate passenger terminals for international and domestic traffic, These opened in 1978 and 1983 respectively. The terminals had boarding concourses running along the length of the terminal. Later on, perpendicular pier could be added, increasing the number of contact stands. At this point, it is unclear if the idea of a south domestic terminal in the long run was retained or if it was dropped from the Master Plan early on. Leave us a comment below if you know the answer!
SLOWER GROWTH
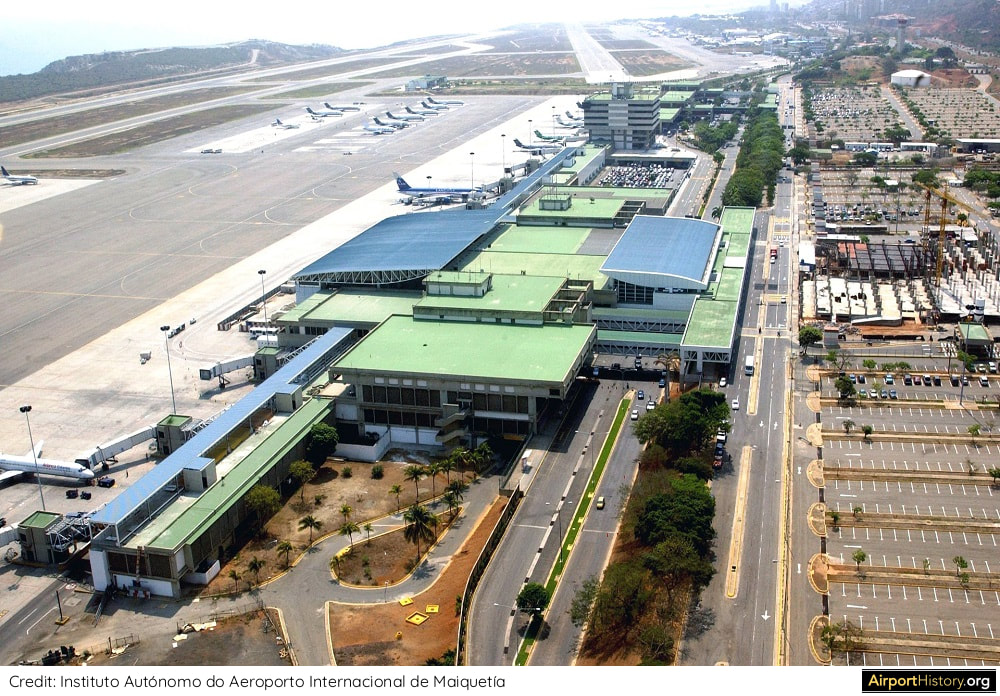
Over the decades, traffic growth was much slower than anticipated. The traffic of 30 million passengers, which had been projected in the late 1960s, was never reached. The record stands at 12.18 million passengers in 2013, after which the economy went into free fall. As a result, the Master Plan was only partially implemented. The parallel runway 09/27 was never built. Also, no additional passenger terminals were added. Instead, in the early 2000s, the existing international terminal was enlarged and re-modelled. The domestic terminal has not been altered, only having been outfitted with new glass-cladded boarding bridges.
The 1968 Maiquetía Master Plan stands testament to a time when the sky was literally the limit for Venezuela. Let's hope these times will return one day!
What are your thoughts on the original plans for Maiquetía? Let us know in the comments below!
More airport articles: click here
Want more stunning airport photos & stories?
Sign up to our newsletter below to know when new content goes online.
1 Comment
Russ Nehrig
29/9/2022 22:04:16
In 1953, my parents took my brother and me to see Chicago Midway, the busiest airport in the world. We stood on the observation deck and were captivated at the sight of people boarding the DC-6s and twin-engine Convairs in the gathering darkness. They told us about The Cloud Room restaurant, where you could see movie stars!
Reply
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
With a title inspired by the setting of the iconic 70s film "Airport", this blog is the ultimate destination for airport history fans.
Categories
All
About me
Marnix (Max) Groot Founder of AirportHistory.org. Max is an airport development expert and historian. |








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed